- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
In the following we show to you how to use ctrlX DRIVE under a Schneider control (using sercos).
Versions used
All the functions and screen shots are based on:
- ctrlX DRIVE Engineering version 01V18
- Runtime / Firmware version of drive AXS-V0308
Prerequisites
A connection to the ctrlX DRIVE has been successfully established, the device is correctly wired and 24 V are successfully put on. As well the engineering tool ctrlX DRIVE Engineering has been started.
1. Configure parameters of Schneider control
The Schneider control needs to be set correctly as following:
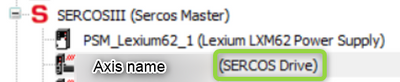
Fig. 1.: Configuration of Schneider control (1) --> use general sercos drive
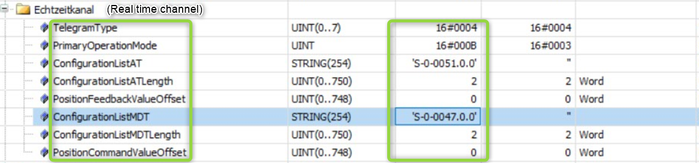
Fig. 2.: Configuration of Schneider control (2) --> uses position control exchanging actual position and command position cyclically
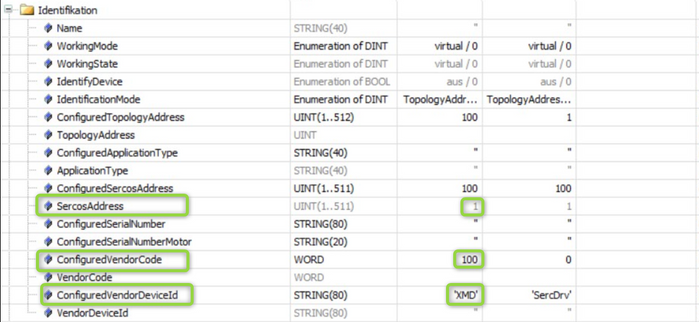
Fig. 3.: Configuration of Schneider control (3) --> set address and vendor information
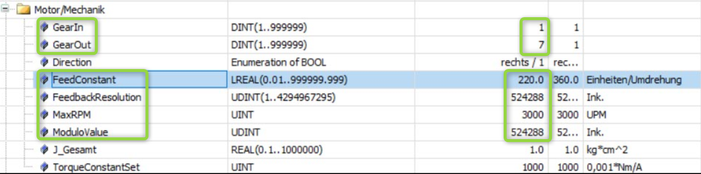
Fig. 4.: Configuration of Schneider control (4) – Settings for a rotatory axis modulo with incremental scaling using a Hiperface multiturn encoder with 4096 revolutions*128 signals/revolution (--> 4096 * 128 = 524 288) using a gear ratio of 1 : 1
Fig. 5.: Configuration of Schneider control (5) – Settings for a linear axis with incremental scaling using a Hiperface multiturn encoder with 4096 revolutions * 128 signals/revolution (--> 4096 * 128 = 524 288) using a gear ratio of 7 : 1
2. Parameterize ctrlX DRIVE
The parameterization of the ctrlX DRIVE should be according to the following guidelines, using
- 0,001° or 0,001 mm
- 0,001 °/s or 0,001 mm/s
- 0,001 rad/s2 or 0,001 mm/s2
as resolution. Mind that you have to correct the travel range, gear ratio and feed constant according to your mechanics and needs.
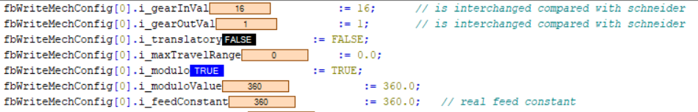
Rotatory axis modulo
On the Schneider control
- the correct gear ratio needs to be entered
- the translatory setting must be “False”
- the maximum travel range needs to be set to “0.0”
- the modulo setting must be “True”
- the modulo value and feed constant needs to be set to “360.0”
Fig. 6.: Configuration of Schneider control (rotatory axis modulo, gear ratio 16)
Fig. 7.: Axis mechanics parameterization of rotatory axis modulo with gear ratio 16 --> if negation needs to be set depends on the mechanical constellations
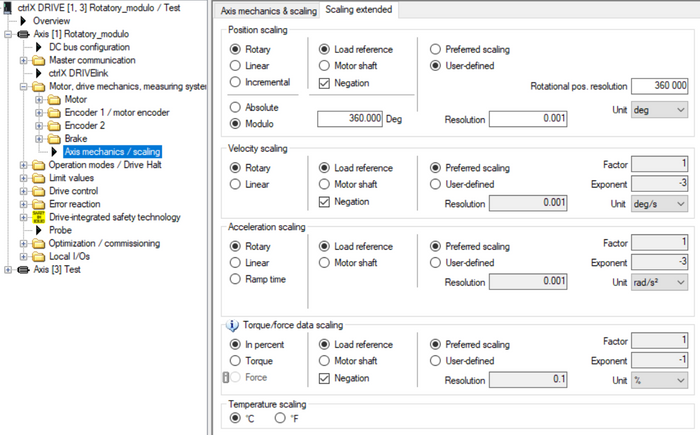
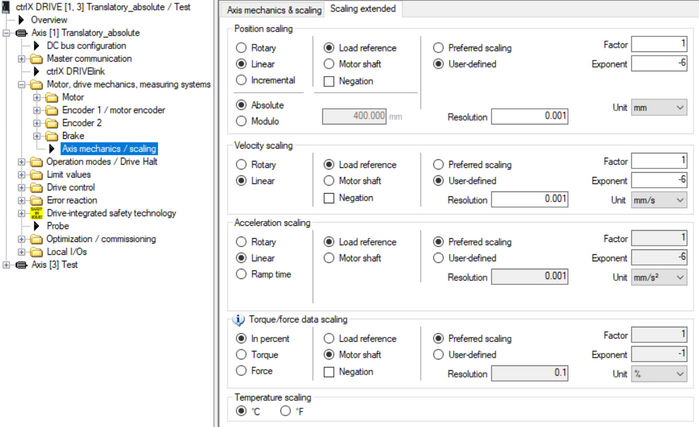
Fig. 8.: Scaling parameterization of rotatory axis modulo
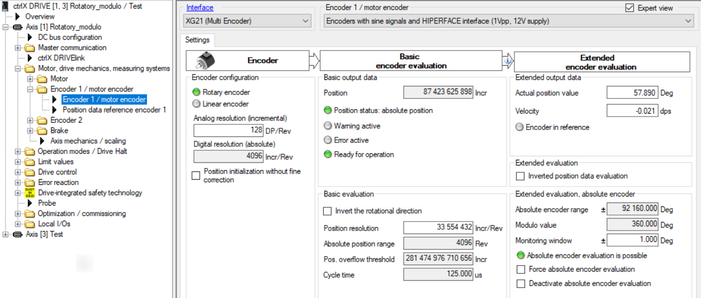
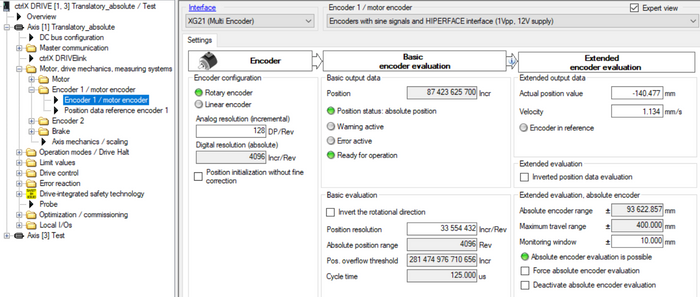
Fig. 9.: Encoder parameterization of rotatory axis modulo with Hiperface encoder
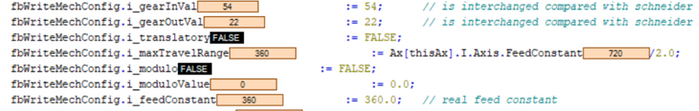
Rotatory axis absolute
On the Schneider control
- the correct gear ratio needs to be entered
- the translatory setting must be “False”
- the maximum travel range and feed constant needs to be set to intended travel range value e.g. “360.0”
- the modulo setting must be “False”
- the modulo value needs to be set to “0.0”
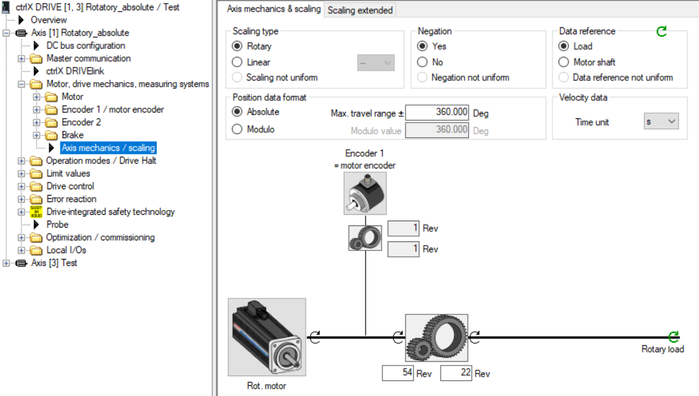
Fig. 10.: Configuration of Schneider control (rotatory axis absolute, gear ratio 54 to 22)
Fig. 11.: Axis mechanics parameterization of rotatory axis absolute with gear ratio 54 to 22 --> if negation needs to be set depends on the mechanical constellations
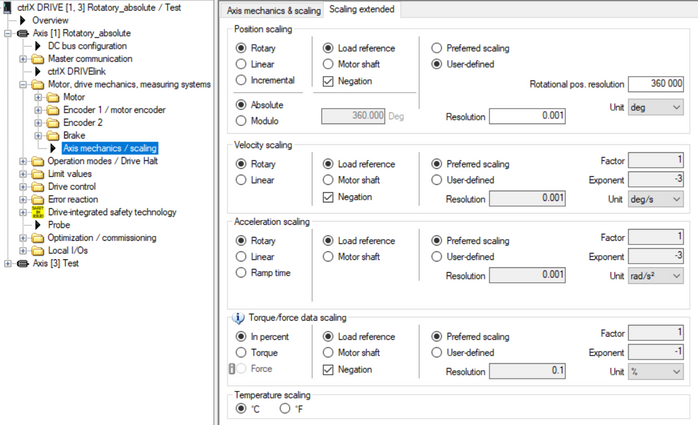
Fig. 12.: Scaling parameterization of rotatory axis absolute
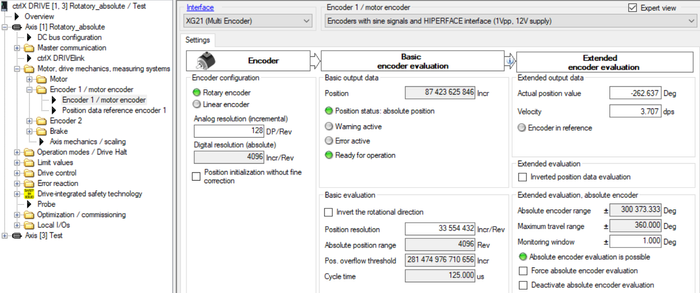
Fig. 13.: Encoder parameterization of rotatory axis absolute with Hiperface encoder
Linear axis modulo
On the Schneider control
- the correct gear ratio needs to be entered
- the translatory setting must be “True”
- the maximum travel range needs to be set to “0.0”
- the modulo setting must be “True”
- the modulo value needs to be set to intended value in here e.g. “127.0”
- the feed constant needs to be set to intended value e.g. “508.0”
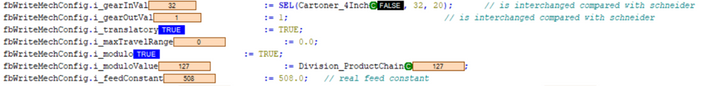
Fig. 14.: Configuration of Schneider control (Translatory axis modulo with gear ratio and feed constant)
Fig. 15.: Axis mechanics parameterization of linear axis modulo with gear ratio 54 to 22 and feed constant 508 mm --> if negation needs to be set depends on the mechanical constellations
Fig. 16.: Scaling parameterization of linear axis modulo
Fig. 17.: Encoder parameterization of linear axis modulo with Hiperface encoder
Linear axis absolute
On the Schneider control
- the correct gear ratio needs to be entered
- the translatory setting must be “True”
- the maximum travel range needs to be set to intended value in here e.g. “400.0”
- the modulo setting must be “False”
- the modulo value needs to be set to “0.0”
- the feed constant needs to be set to intended value e.g. “320.0”
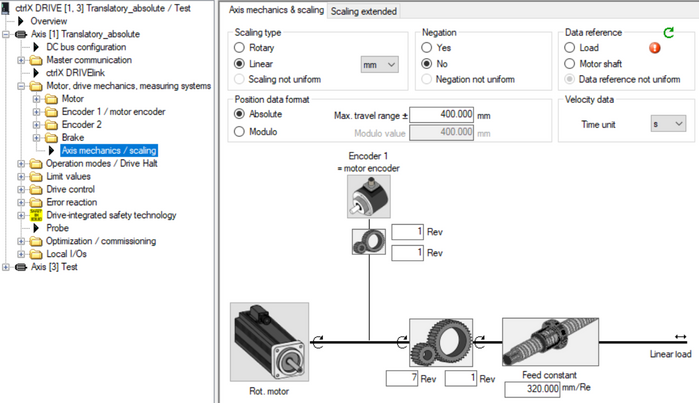
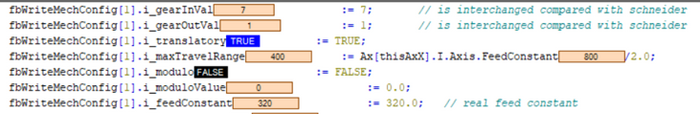
Fig. 18.: Configuration of Schneider control (Translatory axis absolute with gear ratio and feed constant)
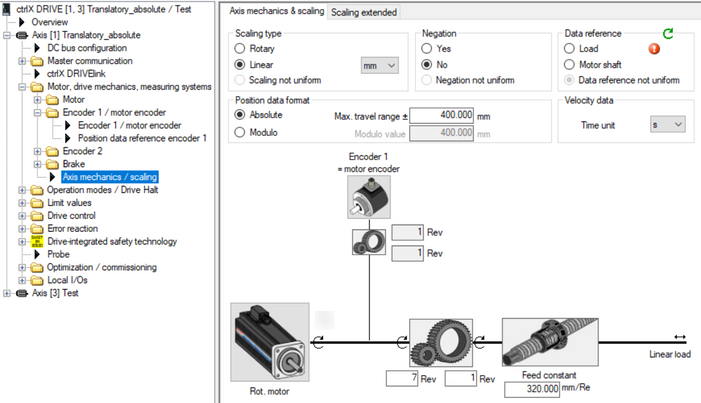
Fig. 19.: Axis mechanics parameterization of linear axis absolute with gear ratio 7 and feed constant 320 mm --> if negation needs to be set depends on the mechanical constellations
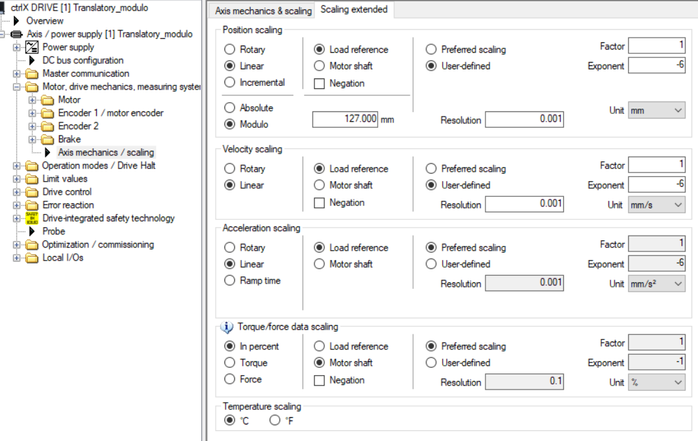
Fig. 20.: Scaling parameterization of linear axis absolute
Fig. 21.: Encoder parameterization of linear axis absolute with Hiperface encoder
Find in attachment some parameter group sets for the different mechanisms as starting point for your parameterization.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.